Air Circuit Breaker Function Introduction
The air circuit breaker mainly has the following functions:
Function | Description |
Current Interruption | Automatically interrupts the current when it exceeds the trip rating of the breaker. |
Protection | Protects electrical circuits from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. |
Safety | Ensures safety by preventing electrical fires and equipment damage. |
Efficiency | Facilitates efficient circuit management and maintenance. |
It is widely used in various power distribution systems for reliable protection and control.
Inquire
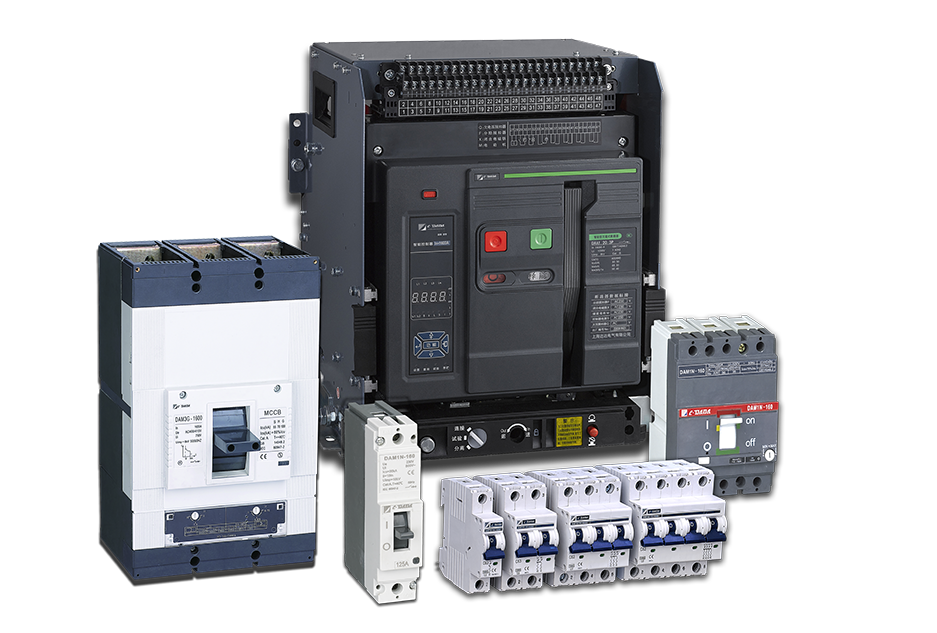
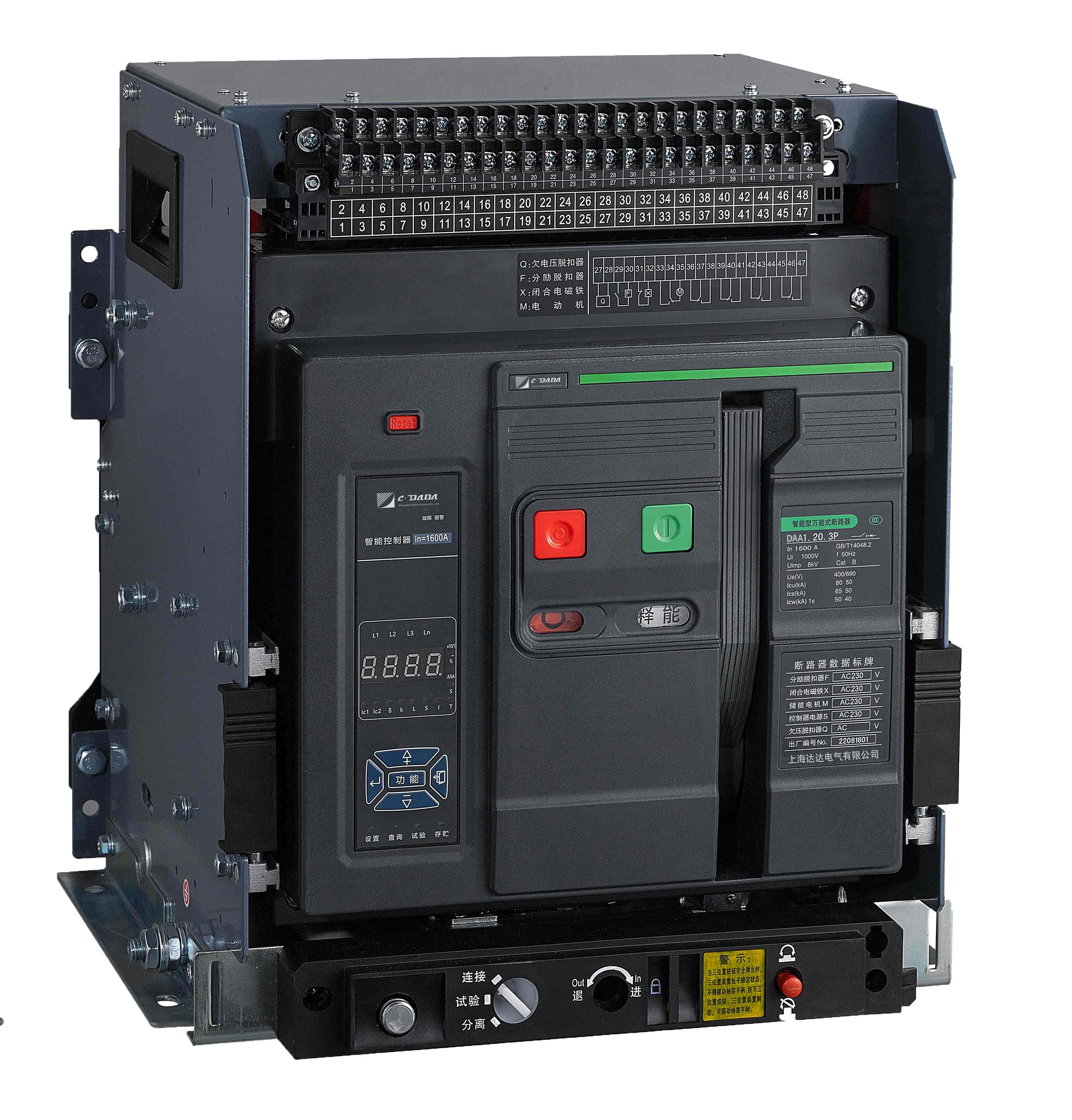
Features of Air circuit breaker
High breaking capacity: ACB can handle high fault currents and is suitable for use in primary distribution systems.
Modular design: ACB has a modular design that allows for easy replacement of components such as trip units, control units, and communication modules.
Multiple protection functions: ACB provides various protection functions such as overcurrent protection, short-circuit protection, ground fault protection, and undervoltage protection.
Adjustable settings: The protection settings of ACB can be adjusted according to the specific requirements of the application, providing flexibility in its usage.
Communication capabilities: Some ACBs are equipped with communication modules that allow for remote monitoring, control, and data logging.
Long service life: ACB is designed for long-term operation with minimal maintenance requirements, ensuring reliable performance over time.
Easy installation and maintenance: ACB has a compact size and can be easily installed in switchgear cabinets.
Wide range of accessories: ACB can be equipped with various accessories such as auxiliary contacts, alarm contacts, and shunt trip devices to enhance its functionality.
Related Solutions
-
 Learn More
Learn MorePower Industry
-
 Learn More
Learn MoreBuilding Automation
Building automation started with simple mechanical controls and has evolved into sophisticated digital systems that integrate various technologies to enhance building performance and occupant comfort.

-
 Learn More
Learn MoreIndustrial Manufacturing
Today, the industry faces new challenges and opportunities, driven by technological advancements, globalization, and changing consumer demands.






 Subscription
Subscription